Treating Wastewater Through Multi-Step Process May 11, 2022
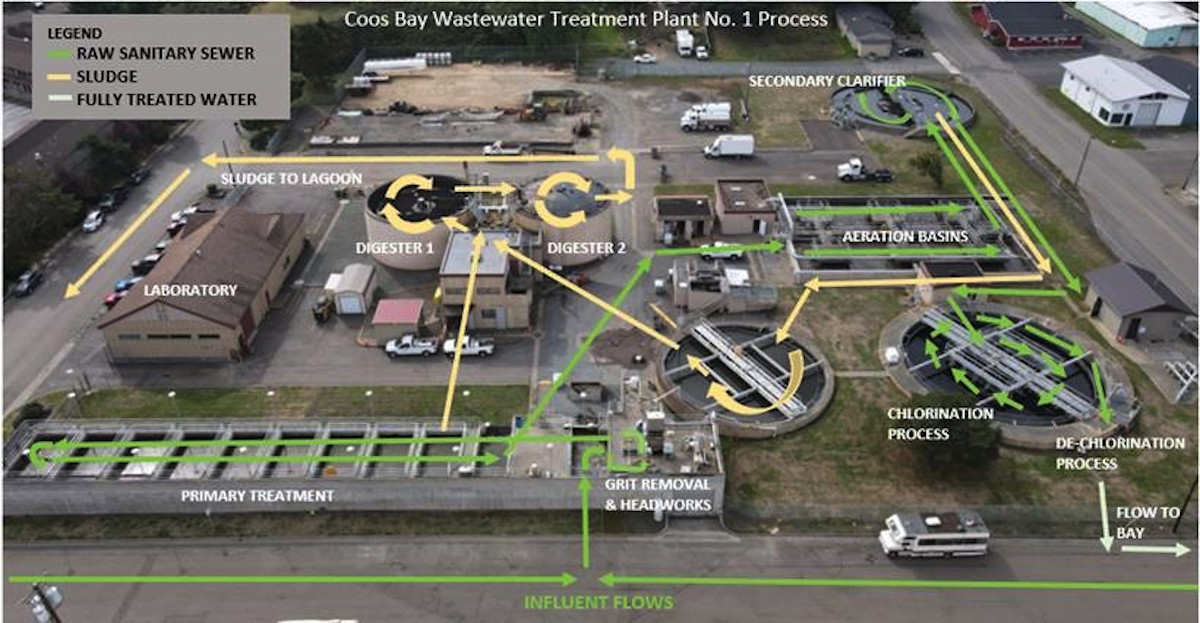
The diagram above illustrates the Wastewater Treatment Plant No. 1 process. Influent flows are what is put into the system by everyone through flushing of toilets, laundry, dishes, bathing, inflow and infiltration, and other drains in homes and businesses. Once the raw sanitary sewer enters the treatment plant, it is put through a process in which all non-treatable items are removed including sand, gravel, feminine hygiene products, wipes, rags, needles, fats oils and grease, etc. The flow then enters primary treatment where more non-treatable items such fats oils and grease are skimmed off the top and solids (poop) settle to the bottom and are sent to the digesters for processing. From the primary treatment, flows enter the aeration basins. These basins are where oxygen is input into the water to help the microorganisms. Microorganisms are a very essential part of the wastewater treatment process as they consume pollutants.
From the aeration basins. the wastewater flows to the secondary clarifier. The secondary clarifier process is in a circular basin where biomass and microorganisms settle to the bottom. This cycle repeats itself until only clean water is left. The wastewater then enters the final step of treatment, which at Plant 1, is chlorination. The chlorine disinfects and kills any remaining material. After the water is chlorinated, it is de-chlorinated prior to flowing to the waterways.
The digesters at Plant 1 are ran in series, meaning that the flow goes to digester 1 and then is transferred to digester 2. The digesters heat and mix the solids to reduce and stabilize the solids. Once this process is complete, the sludge is then sent to the lagoon in eastside. A lagoon is a large, lined pond used as a containment area where sludge is stored and further broke down by organisms in the lagoon. During the summer months, the lagoon is dredged and the biosolids are land applied to local farmland as fertilizer. Biosolids are a beneficial resource containing essential plant nutrients and organic matter that is used as fertilizer.
At many times during this treatment process tests are conducted. Samples are taken and processed in the onsite lab or sent out to outside labs daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly and yearly to meet permit requirements. The National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) permits control water pollution by regulating point sources that discharge pollutants into waters of the United States.

